Describe the Process of Crossing Over in Meiosis
Meiosis and genetic diversity. It is in the prophase of meiosis I that crossing over of the chromosomes takes place and the homologous chromosomes are separated into two daughter cells.

The Process Of Meiosis Boundless Biology Biology Lessons Meiosis Biology Notes
Describe the process of cell division in somatic and reproductive cells Mitosis Asexual reproduction of body cells identical G1 growth period organelles begin to double in number S nuclear DNA replicates G2 second growth phase synthesis of proteins Mitosis o Interphase centrioles in centrosomes duplicated chromatin condensing o Prophase.

. Contrast the events of meiosis I and meiosis II with the events of mitosis. After some time the synapses snap finishing the process of crossing over of the genetic information. Then exchange of a small segment of chromatid genetic material between non sister chromatids takes place.
This problem has been solved. Then drag and drop the sentences into the correct chronological order meiosis I Drag the text blocks below into their correct order. If they fail to separate normally it is called the non-disjunction of chromosomes.
Work Saved Help Save Exit Submit Complete the following sentences to describe the process of crossing-over during meiosis. Either of the two strands of a chromosome that separate during meiosis. Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces four haploid gametes from a.
When did the chromosomes cross. This process occurs during the prophase of meiosis I. The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes that results in recombinant chromosomes.
The meiosis I division is also known as reduction division. The 2 sister chromatids intersect and exchange some of their genetic material. Crossing over is the swapping of genetic material that occurs in the germ line.
Crossing over meiosis I meiosis II and genetic variation. In meiosis II the sister chromatids are pulled apart from each other to give rise to four haploid daughter cells. This is because it involves the formation of two daughter nuclei with just half number of chromosomes as that present in the another cell.
Meiosis or reduction division is a nuclear division process that. Meiosis takes place in male and female. Basically the crossing over of genetic material between the non-sister chromatids occurs in this phase.
Chromosomal crossover in meiosis I. More over in the prophase stage of meiosis crossing over interchange of chromosome segments between two homologous chromosomes takes place. To the haploid n number.
The process which results in recombination by exchange of the segments between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes is called as crossing over. Reduces the chromosome number of a diploid 2n cell by half ie. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half.
It takes place in pachytene stage of prophase-I of meiosis. Crossing over results in a shuffling of genetic material and is an important cause of the genetic. Describe the process of meiosis and recognize events that occur during each event B.
Describe the process of crossing over AND identify the phase of meiosis when crossing over occurs. Phenomenon that occurs in Prophase I of meiosis between 2 sister chromatids on different chromosomes of an Homologous pair. During the formation of egg and sperm cells also known as meiosis paired chromosomes from each parent align so that similar DNA sequences from the paired chromosomes cross over one another.
- homologous chromosomes wrap around one-another at bivalent. See the answer See the answer done loading. The process of crossing over occurs during meiosis.
The normal separation of homologous chromosomes is called the disjunction of chromosomes. Meiosis is composed of two successive cell divisions. Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosome pairs exchange segments or parts and Chiasma is formed in these exchanged regions.
During prophase of meiosis I the paternal homologous chromosome is paired with the maternal homologous chromosome. Crossing over can be observed visually after the exchange as chiasmata singular chiasma. - therefore whilst genes remain same alleles at each loci may vary following cross over.
The errors in meiosis occur during the process of crossing-over and separation of homologous chromosomes. Crossing over occurs between these. Nonsister These chromosomes stay close together and exchange genetic material an event also known.
Crossing over events dring meiosis help produce genetic variation. Define the term meiosis. Crossing over is the process of swapping DNA sequences between the chromatids of paired homologous chromosomes.
The synaptonemal complex supports the exchange of chromosomal segments between non-sister homologous chromatids a process called crossing over. Describe the process of crossing over in prophase 1 of meiosis. - tension builds equivalent portions of DNA break off swap with one-another.
Crossing over creates genetic variation by exchanging DNA between two nonsister chromatids to produce genetically unique chromosomes. Describe the significant of crossing over synapsis and independent assortment C. Describe the process of meiosis highlighting the changein chromosome number and structure after each.
A meiosis I reduction division. It results new combinations of genes which causes variation in offspring. Gametes zygotes haploid diploid.
Define gene diploid haploid gamete ovum sperm and crossing over. Phases of meiosis I. This is called a bivalent and is composed of two copies of the paternal chromosome and two copies of the maternal one.
Describe the difference and similarities between mitosis and meiosis D. Non sister chromatids overlap or coil each other. Describe the process of Crossing Over during Prophase I of Meiosis indicating what is being exchanged which chromosomes are involved and include the terms synapsis tetrad and chiasmata in your description.
Two pairs of sister chromatids a dyad pair aligned in a certain way and often on the equatorial plane during the meiosis process. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. The process of exchange of genetic material between non sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes is known as crossing over.

Meiosis Is Required In The Maintenance Of Chromosome Number As Well As Bring About An Increase In Genetic Diversity Meiosis Genetic Variation Molecular Biology

Crossing Over Definition And Functions Biology Dictionary Genetics Daughter Cells Biology

Meiosis Guided Reading Worksheets Print Google Versions Meiosis Guided Reading Worksheets Middle School Science Resources

10 Meiosis Reading Worksheet Reading Worksheets Mitosis Activity Worksheets Meiosis

Cell Cycle Mitosis And Meiosis Meiosis Cell Cycle Mitosis

Meiosis Crossing Over Students Britannica Kids Homework Help

Meiosis Part 2 Modeling Crossing Over In 2021 Meiosis Genetic Variation Tenth Grade
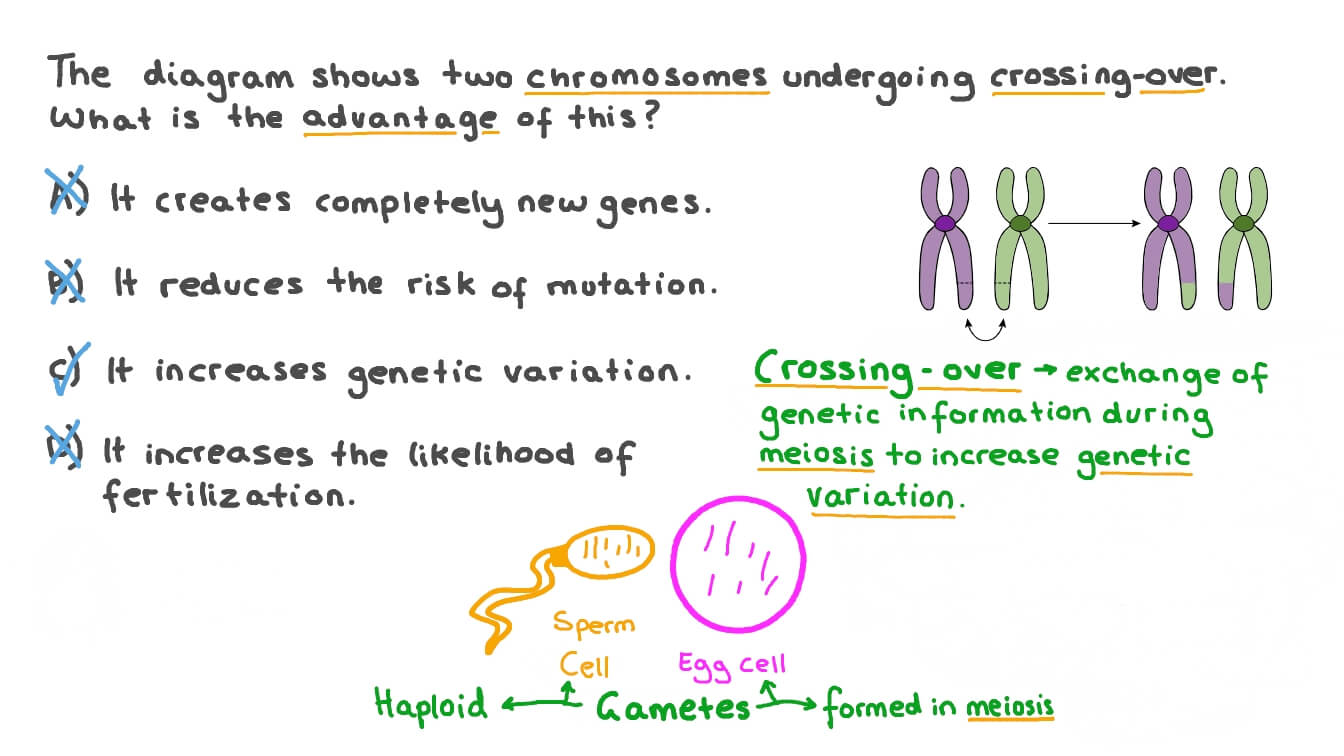
Question Video Understanding The Role Of Crossing Over In Meiosis Nagwa

The Process Of Meiosis Boundless Biology Meiosis Biology Biology Notes

What Is Crossing Over In Meiosis Crossing Over Example Recombination Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Genetics Meiosis Chromosome Crossover Genetic Variation High School Biology Genetic Variation Meiosis Genetics

Catatan Biologi Meiosis Panduan Belajar Biokimia Mitosis

Difference Between Mitosis And Meiosis Mitosis Meiosis Biochemistry Notes

Meiosis Stages Phases Of Meiosis 1 And 2 With Diagrams Jotscroll Meiosis Somatic Cell Meiosis Stages Diagram

The Process Of Meiosis Boundless Biology Teaching Biology Study Biology Biology Lessons

Variations In Meiosis The Parthenogenetic Lizards Ricochet Science Biology Teacher Meiosis Biology Classroom

Synapsis Or Crossing Over Mechanism For Increasing Genetic Diversity Meiosis And Other Factors Affecting Genetic Variability Mcat Content
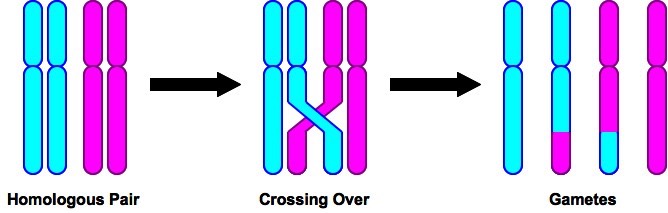
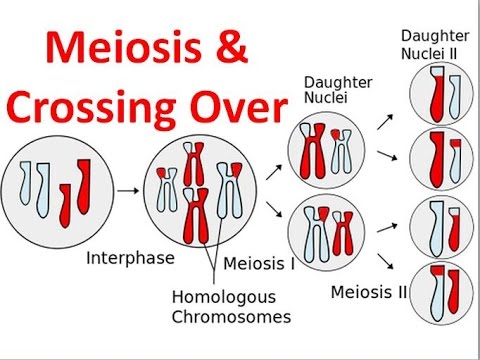
Comments
Post a Comment